离线推理( offline inference )场景中,比较关注最大化吞吐量并降低单次推理成本。传统方法往往是资源消耗大、速度慢、容易出现性能瓶颈、导致云服务开支较高。需要专为大语言模型优化的推理部署引擎。
下面 LLM 的两种离线推理部署性能对比:vLLM vs HuggingFace.
HuggingFace Transformers
HuggingFace 的 Transformers 库已经是 LLM 领域标准工具,其具有API接口统一、模型库庞大、开箱即用等特性。
离线部署场景,HuggingFace 提供了直观的工作流程:
- 模型 和 tokenizer 加载
- 循环或者批量方式,处理输入数据。
但是,其存在明显瓶颈,尤其是在未进行专门优化的情况下:顺序处理机制、相对抵消的内存管理(尤其是注意力的 key 和 value 缓存的管理) 会显著影响性能。
虽然 HuggingFace 的 Transformers 库具有较高的灵活性,但是面对与大规模离线推理场景,会存在效率问题。
典型的推理代码如,
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
MODEL_NAME = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"
# Load model and tokenizer
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME, device_map="auto")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
MODEL_NAME,
padding_side="left",
truncation_side="left"
)
# Set pad_token (LLaMA doesn't define one by default)
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
# Define batch of user prompts (4 in total)
user_questions = [
"What is Thailand's national food symbol?",
"What is the capital of Norway?",
"Who invented the telescope?",
"What is the chemical symbol for gold?"
]
# Format messages in chat format
messages_batch = [
[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Respond in two sentences."},
{"role": "user", "content": question}
]
for question in user_questions
]
# Tokenize using chat template with padding and truncation
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages_batch,
tokenize=True,
return_tensors="pt",
padding=True,
truncation=True,
max_length=2048
).to(model.device)
# Clear previous GPU stats (optional, but good practice for clean runs)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# Generate responses
input_length = input_ids.shape[1]
generated_ids = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
max_new_tokens=128,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.pad_token_id
)
# Decode outputs
decoded_outputs = tokenizer.batch_decode(
generated_ids[:, input_length:],
skip_special_tokens=True
)vLLM
vLLM 是专为吞吐量和效率而设计。其核心创新在于PagedAttention技术,该技术能够高效管理注意力中的 key 和 value 对内存。
注意力中的 key 和 value 对内存管理,对于离线推理是至关重要的,因为,键值缓存(KV cache) 会消耗大量的 GPU 显存,尤其是在处理长序列和大批量数据时。PagedAttention创新性的将 KV cache 内存看作是分页(pages),并采用类似于操作系统虚拟内存的机制,实现内存分配和回收。该技术显著减少了内存碎片化,有效提升批量大小。
此外,vLLM 还整合多想创新技术,如,
- 连续批处理Continuous Batching:实时处理动态请求流,通过即时响应新任务而非等待满批处理,显著提升GPU利用率。该技术通常用在 online serving,但是对于离线部署中处理不同长度的连续提示序列也同样高效。
- 快速模型执行Fast Model Execution:利用CUDA/HIP计算图技术来优化 kernel 执行。
- 量化支持 Quantization Support:同 GPTQ、AWQ、INT4、INT8、FP8 等多种量化方案,有效降低显存占用,提升推理速度。
- 优化的 CUDA内核 Optimized CUDA Kernels:集成 FlashAttention、FlashInfer等高性能Kernels,实现底层运算加速。
灵活性和易用性方面,vLLM 同样具有如下优势:
- 无缝兼容 HuggingFace 模型
- 支持多种加码算法,如采样sampling、束搜索beam search等
- 分部署推理,支持张量并行tensor parallelism 和流水线并行pipeline parallelism
- 内置 OpenAI-compatible API 服务接口
- 支持多种硬件,如NVIDIA、AMD、Intel 等,以及专用的AI加速器等
典型的推理代码如,
import torch
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
# Initialize tokenizer separately to apply chat template
MODEL_NAME = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME)
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token # Just in case
# Define a batch of prompts (4 in total)
user_questions = [
"What is Thailand's national food symbol?",
"What is the capital of Norway?",
"Who invented the telescope?",
"What is the chemical symbol for gold?"
]
# Create structured chat messages
messages_batch = [
[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Respond in two sentences."},
{"role": "user", "content": question}
]
for question in user_questions
]
# Manually apply chat template to each prompt
rendered_prompts = [
tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False)
for messages in messages_batch
]
# Define generation parameters
sampling_params = SamplingParams(max_tokens=128)
# Initialize vLLM
llm = LLM(
model=MODEL_NAME,
max_model_len=2048,
)
# Run batch generation
outputs = llm.generate(rendered_prompts, sampling_params)性能对比
实验环境:
- Google Vertex AI Workbench
- GPU(s): NVIDIA L4 with 24GB VRAM.
- Python: 3.10 (managed via Conda environment)
- Model: meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct
- accelerate==1.2.1
- bitsandbytes==0.45.0
- PyTorch with CUDA 12.1: torch @ https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121_full/torch-2.5.1%2Bcu121-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl
- transformers==4.47.1
实现结果:
对比在不同批量大小下的推理耗时,模拟典型离线推理工作负载。如:
| Batch Size | vLLM IFT(sec) | HuggingFace IFT (sec) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2.32 | 5.32 |
| 8 | 2.51 | 7.24 |
| 16 | 3.01 | 9.50 |
| 32 | 3.38 | 12.90 |
IFT = Inference Time
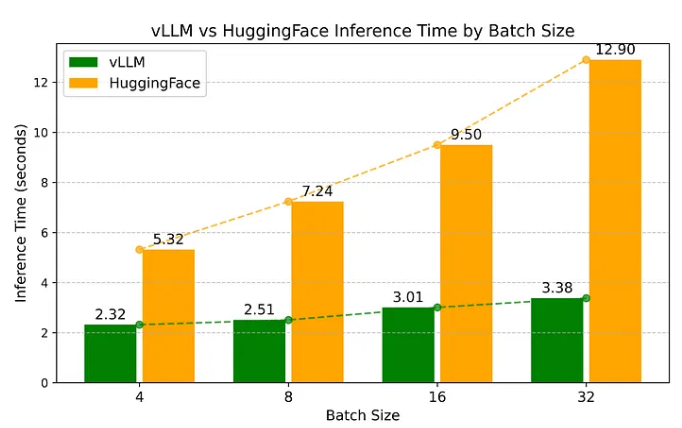
关键结果:
- vLLM 在批量任务中,速度是 HuggingFace 的 2-4 倍
- vLLM 采用 PagedAttention 优化 KV cache 内存
- vLLM 对于大规模推理具有更好的可扩展性和GPU利用率
总结
- vLLM 更适合于生产环境的高吞吐、高性能离线部署
- HuggingFace 在算法研究和原型开发中灵活性更好