Github - ultralytics/yolov5
yolov5/detect.py - https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py
Yolov5 的检测示例, 如:
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --img 416 --conf 0.4 --source inference/images/
结果例图:
1. 数据加载
yolov5 detect.py 支持多种输入,如:images, videos, directories, webcams, rtsp 和 http streams.
python detect.py \ --source file.jpg # image file.mp4 # video dir/ # directory 0 # webcam 'rtsp://170.93.143.139/rtplive/470011e600ef003a004ee33696235daa' # rtsp 'http://112.50.243.8/PLTV/88888888/224/3221225900/1.m3u8' # http
对应的包含两个数据加载 Dataloader 函数:LoadStreams() 和 LoadImages().
1.1. LoadStreams
class LoadStreams: # multiple IP or RTSP cameras
def __init__(self, sources='streams.txt', img_size=640):
self.mode = 'images'
self.img_size = img_size
# 多个 sources 源
if os.path.isfile(sources):
with open(sources, 'r') as f:
sources = [x.strip() for x in f.read().splitlines() if len(x.strip())]
else:
sources = [sources]
n = len(sources)
self.imgs = [None] * n
self.sources = sources
for i, s in enumerate(sources):
# 启动视频流读取线程.
print('%g/%g: %s... ' % (i + 1, n, s), end='')
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(eval(s) if s.isnumeric() else s)
assert cap.isOpened(), 'Failed to open %s' % s
w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) % 100
_, self.imgs[i] = cap.read() # guarantee first frame
thread = Thread(target=self.update, args=([i, cap]), daemon=True)
print(' success (%gx%g at %.2f FPS).' % (w, h, fps))
thread.start()
print('') # newline
# check for common shapes
# 检验所有输入图像的shapes
s = np.stack([letterbox(x, new_shape=self.img_size)[0].shape for x in self.imgs], 0) # inference shapes
self.rect = np.unique(s, axis=0).shape[0] == 1 # rect inference if all shapes equal
if not self.rect:
print('WARNING: Different stream shapes detected. For optimal performance supply similarly-shaped streams.')
def update(self, index, cap):
# 守护线程中读取下一帧
# Read next stream frame in a daemon thread
n = 0
while cap.isOpened():
n += 1
# _, self.imgs[index] = cap.read()
cap.grab() #抓取视频帧
if n == 4: # read every 4th frame
_, self.imgs[index] = cap.retrieve()
n = 0
time.sleep(0.01) # wait time
def __iter__(self):
self.count = -1
return self
def __next__(self):
self.count += 1
img0 = self.imgs.copy()
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
raise StopIteration
# Letterbox
img = [letterbox(x, new_shape=self.img_size, auto=self.rect)[0] for x in img0]
# Stack
img = np.stack(img, 0)
# Convert
img = img[:, :, :, ::-1].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) # BGR to RGB, to bsx3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return self.sources, img, img0, None
def __len__(self):
return 0 # 1E12 frames = 32 streams at 30 FPS for 30 years1.2. LoadImages
用于模型预测.
img_formats = ['.bmp', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.tif', '.tiff', '.dng']
vid_formats = ['.mov', '.avi', '.mp4', '.mpg', '.mpeg', '.m4v', '.wmv', '.mkv']
class LoadImages: # for inference
def __init__(self, path, img_size=640):
p = str(Path(path)) # os-agnostic
p = os.path.abspath(p) # absolute path
if '*' in p:
files = sorted(glob.glob(p, recursive=True)) # glob
elif os.path.isdir(p):
files = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(p, '*.*'))) # dir
elif os.path.isfile(p):
files = [p] # files
else:
raise Exception('ERROR: %s does not exist' % p)
images = [x for x in files if os.path.splitext(x)[-1].lower() in img_formats]
videos = [x for x in files if os.path.splitext(x)[-1].lower() in vid_formats]
ni, nv = len(images), len(videos)
self.img_size = img_size
self.files = images + videos
self.nf = ni + nv # number of files
self.video_flag = [False] * ni + [True] * nv
self.mode = 'images'
if any(videos):
self.new_video(videos[0]) # new video
else:
self.cap = None
assert self.nf > 0, 'No images or videos found in %s. Supported formats are:\nimages: %s\nvideos: %s' % \
(p, img_formats, vid_formats)
def __iter__(self):
self.count = 0
return self
def __next__(self):
if self.count == self.nf:
raise StopIteration
path = self.files[self.count]
if self.video_flag[self.count]:
# 视频文件读取
self.mode = 'video'
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
if not ret_val:
self.count += 1
self.cap.release()
if self.count == self.nf: # last video
raise StopIteration
else:
path = self.files[self.count]
self.new_video(path)
ret_val, img0 = self.cap.read()
self.frame += 1
print('video %g/%g (%g/%g) %s: ' % (self.count + 1, self.nf, self.frame, self.nframes, path), end='')
else:
# Read image
self.count += 1
img0 = cv2.imread(path) # BGR
assert img0 is not None, 'Image Not Found ' + path
print('image %g/%g %s: ' % (self.count, self.nf, path), end='')
# Padded resize
img = letterbox(img0, new_shape=self.img_size)[0]
# Convert
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# cv2.imwrite(path + '.letterbox.jpg', 255 * img.transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]) # save letterbox image
return path, img, img0, self.cap
def new_video(self, path):
self.frame = 0
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(path)
self.nframes = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
def __len__(self):
return self.nf # number of files1.3. 辅助函数
def load_image(self, index):
# loads 1 image from dataset, returns img, original hw, resized hw
img = self.imgs[index]
if img is None: # not cached
path = self.img_files[index]
img = cv2.imread(path) # BGR
assert img is not None, 'Image Not Found ' + path
h0, w0 = img.shape[:2] # orig hw
r = self.img_size / max(h0, w0) # resize image to img_size
if r != 1: # always resize down, only resize up if training with augmentation
interp = cv2.INTER_AREA if r < 1 and not self.augment else cv2.INTER_LINEAR
img = cv2.resize(img, (int(w0 * r), int(h0 * r)), interpolation=interp)
return img, (h0, w0), img.shape[:2] # img, hw_original, hw_resized
else:
return self.imgs[index], self.img_hw0[index], self.img_hw[index] # img, hw_original, hw_resized
#
def letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):
# 将图像尺寸调整为 32像素倍数的矩形.
# Resize image to a 32-pixel-multiple rectangle https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # 仅缩小,不放大 only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, 32), np.mod(dh, 32) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)2. 模型加载
根据给定 weights 权重文件,加载模型:
# Load model
model = attempt_load(weights, map_location=device) # load FP32 model
if half:
model.half() # to FP162.1. attempt_load 模型加载函数
class Ensemble(nn.ModuleList):
# Ensemble of models
def __init__(self):
super(Ensemble, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x, augment=False):
y = []
for module in self:
y.append(module(x, augment)[0])
# y = torch.stack(y).max(0)[0] # max ensemble
# y = torch.cat(y, 1) # nms ensemble
y = torch.stack(y).mean(0) # mean ensemble
return y, None # inference, train output
def attempt_load(weights, map_location=None):
# Loads an ensemble of models weights=[a,b,c] or a single model weights=[a] or weights=a
model = Ensemble()
for w in weights if isinstance(weights, list) else [weights]:
# attempt_download(w) # 权重文件下载
model.append(torch.load(w, map_location=map_location)['model'].float().fuse().eval()) # load FP32 model
# Compatibility updates
for m in model.modules():
if type(m) in [nn.Hardswish, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6]:
m.inplace = True # pytorch 1.7.0 compatibility
elif type(m) is Conv:
m._non_persistent_buffers_set = set() # pytorch 1.6.0 compatibility
if len(model) == 1:
return model[-1] # return model
else:
print('Ensemble created with %s\n' % weights)
for k in ['names', 'stride']:
setattr(model, k, getattr(model[-1], k))
return model # return ensemble3. 模型预测
在数据 Dataloader 和模型加载后,进行模型预测.
3.1. 预跑一次预测
在对测试数据进行正式预测前,yolov5 还有一些简单的处理,主要为:
# 验证输入图像的尺寸
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=model.stride.max()) # check img_size
# 预跑一次预测
img = torch.zeros((1, 3, imgsz, imgsz), device=device) # init img
_ = model(img.half() if half else img) if device.type != 'cpu' else None # run once其中,check_img_size 函数实现如:
def make_divisible(x, divisor):
# Returns x evenly divisible by divisor
return math.ceil(x / divisor) * divisor
def check_img_size(img_size, s=32):
# 验证 img_size 是否为步长 s 的倍数.
# Verify img_size is a multiple of stride s
new_size = make_divisible(img_size, int(s)) # ceil gs-multiple
if new_size != img_size:
print('WARNING: --img-size %g must be multiple of max stride %g, updating to %g' % (img_size, s, new_size))
return new_size3.2. 正式预测
# dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz)
#or:
# dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz)
for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
# Inference
pred = model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0]
# Apply NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, opt.conf_thres, opt.iou_thres, classes=opt.classes, agnostic=opt.agnostic_nms)
# Process detections
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per image
if webcam: # batch_size >= 1
p, s, im0 = path[i], '%g: ' % i, im0s[i].copy()
else:
p, s, im0 = path, '', im0s
gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh
if det is not None and len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# vis results
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
label = '%s %.2f' % (names[int(cls)], conf)
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)3.3. non_max_suppression
yolov5 中的 NMS 处理
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6, merge=False, classes=None, agnostic=False):
"""
Performs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results
Returns:
detections with shape: nx6 (x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, cls)
"""
nc = prediction[0].shape[1] - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_det = 300 # maximum number of detections per image
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label = nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
t = time.time()
output = [None] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# If none remain process next image
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n:
continue
# Sort by confidence
# x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)]
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torch.ops.torchvision.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres)
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
try: # update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
except: # possible CUDA error https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/1139
print(x, i, x.shape, i.shape)
pass
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
break # time limit exceeded
return output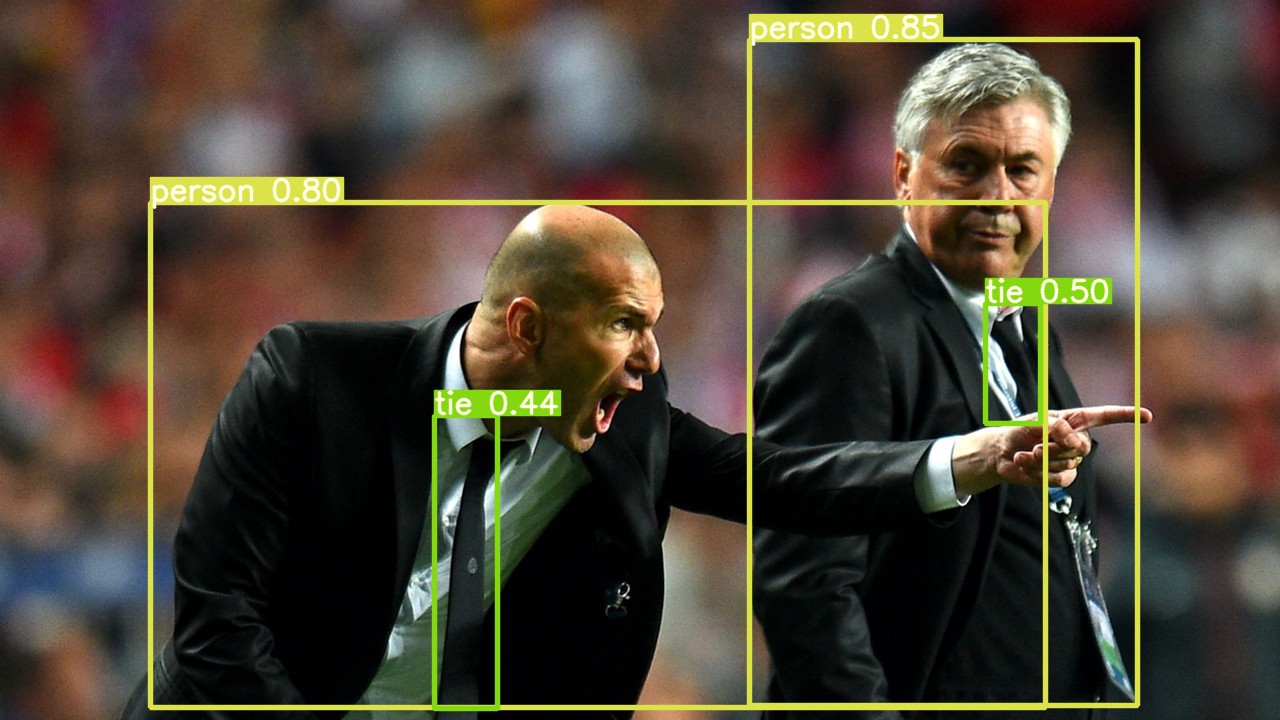
4 comments
测试完没有生成有标注的图片,然后提示:
detect.py: error: unrecognized arguments: --sources ./data/images/
这是为什么呀
输入参数有误,没有识别参数 --sources ./data/images/
你好,rstp地址输入会assert错误提示cap 打不开,怎么解决呢
具体报错是什么?ffmpeg 能正常读取 rstp 流吗?